Nutrition for Chronic Disease Management: Supporting Healing and Recovery
Hey there, my young and curious friends of 2024! It’s your favorite nutrition explorer, Nita Sharda, here to take you on an exciting journey into the world of nutrition and chronic disease management. Now, I know what you might be thinking – “Chronic diseases? Isn’t that something only old people have to worry about?” But trust me, understanding how the foods we eat can impact our health and support healing and recovery is important for everyone, no matter what age we are.
Today, we’re going to put on our explorer hats and discover how nutrition can play a powerful role in managing chronic diseases and supporting overall health and wellbeing. But before we dive in, let me make one thing clear – this is not about putting anyone on a strict diet or making them feel bad about what they eat. It’s simply about empowering you with the knowledge and tools to make food choices that support your health, now and in the future.
So, are you ready to join me on this nutrition and chronic disease adventure? Let’s go!
What are Chronic Diseases?
First things first, let’s talk about what chronic diseases actually are. Chronic diseases are health conditions that last for a long time – usually three months or more – and can often be managed but not cured. Some common examples of chronic diseases include:
- Diabetes
- Heart disease
- Cancer
- Asthma
- Arthritis
While chronic diseases are more common in older adults, they can affect people of all ages, including kids and teens. In fact, the rates of some chronic diseases, like type 2 diabetes and obesity, are on the rise in young people.
But here’s the good news – many chronic diseases can be prevented or managed through healthy lifestyle choices, including good nutrition. By eating a balanced diet that’s rich in whole, minimally processed foods, we can give our bodies the nutrients they need to function at their best and support healing and recovery.
The Role of Nutrition in Chronic Disease Management
So, how exactly does nutrition play a role in chronic disease management? Let’s take a closer look.
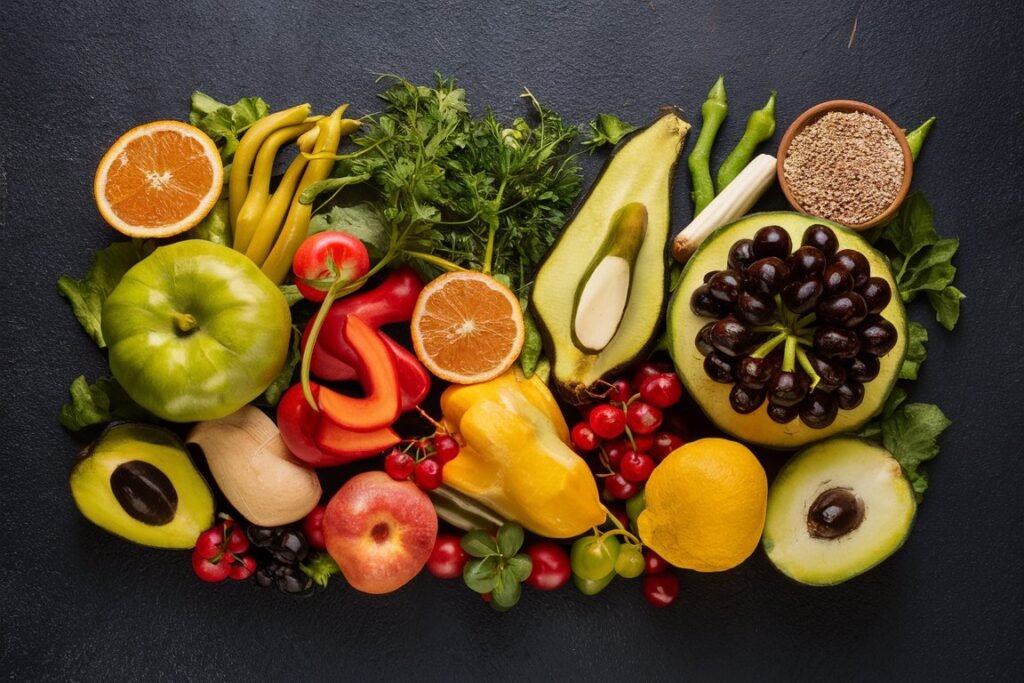

Reducing Inflammation
One of the key ways that nutrition can support chronic disease management is by reducing inflammation in the body. Inflammation is a normal immune response that helps our bodies fight off infections and heal from injuries. But when inflammation becomes chronic, it can contribute to the development and progression of many chronic diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Certain foods, like processed meats, refined grains, and sugary drinks, can promote inflammation in the body. But other foods, like colorful fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, can help reduce inflammation and support overall health.
For example, fatty fish like salmon and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties. Berries, like strawberries and blueberries, are packed with antioxidants that can help protect our cells from damage and reduce inflammation. And spices like ginger and turmeric have been shown to have potent anti-inflammatory effects.
Supporting Gut Health
Another way that nutrition can support chronic disease management is by promoting a healthy gut. Our gut is home to trillions of bacteria, known as the gut microbiome, that play a key role in our overall health and wellbeing. When our gut microbiome is out of balance, it can contribute to chronic diseases like obesity, diabetes, and even mental health conditions like depression and anxiety.
But by eating a diet that’s rich in fiber-rich foods, like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, we can support the growth of healthy gut bacteria and promote a balanced gut microbiome. Fermented foods, like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut, are also great sources of beneficial gut bacteria.
On the other hand, a diet that’s high in processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats can disrupt the balance of our gut microbiome and contribute to chronic disease risk. So, by focusing on whole, minimally processed foods and including plenty of fiber-rich options, we can support our gut health and reduce our risk of chronic diseases.
Managing Blood Sugar
For people with diabetes, managing blood sugar levels is a key part of chronic disease management. And nutrition plays a big role in this process.
When we eat foods that are high in carbohydrates, like bread, pasta, and sugary snacks, our blood sugar levels can rise quickly. This can be especially problematic for people with diabetes, who may have trouble producing or using insulin effectively to manage their blood sugar levels.
But by focusing on low-glycemic foods, which are foods that are slowly absorbed and cause a gradual rise in blood sugar, people with diabetes can better manage their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of complications. Some examples of low-glycemic foods include:
- Non-starchy vegetables like broccoli, spinach, and bell peppers
- Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat bread
- Legumes like lentils, chickpeas, and black beans
- Nuts and seeds like almonds, chia seeds, and flaxseeds
By incorporating more of these low-glycemic foods into their diets, people with diabetes can support healthy blood sugar management and reduce their risk of chronic disease complications.
Providing Essential Nutrients
Finally, nutrition can support chronic disease management by providing our bodies with the essential nutrients they need to function at their best. When we’re dealing with a chronic disease, our bodies may have increased nutrient needs or may have trouble absorbing certain nutrients effectively.
For example, people with inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis may have trouble absorbing nutrients like iron, calcium, and vitamin D. This can lead to nutrient deficiencies that can further complicate their condition and impact their overall health.
But by focusing on nutrient-dense foods and working with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian, people with chronic diseases can ensure they’re getting the nutrients they need to support healing and recovery. Some examples of nutrient-dense foods include:
- Leafy green vegetables like spinach, kale, and collard greens
- Colorful fruits like berries, citrus fruits, and melon
- Lean proteins like chicken, fish, and legumes
- Healthy fats like avocado, nuts, and seeds
- Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat bread
By incorporating a variety of these nutrient-dense foods into their diets, people with chronic diseases can support their bodies’ natural healing processes and promote overall health and wellbeing.
Putting It All Together: A Nutritious Diet for Chronic Disease Management
So, what does a nutritious diet for chronic disease management actually look like? Here are some tips to help you get started:
- Focus on whole, minimally processed foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Include plenty of fiber-rich foods to support gut health and promote feelings of fullness and satisfaction.
- Choose low-glycemic foods to help manage blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of chronic disease complications.
- Incorporate anti-inflammatory foods like fatty fish, berries, and spices to reduce inflammation in the body.
- Work with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to ensure you’re getting the nutrients you need to support healing and recovery.
Remember, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach to nutrition and chronic disease management. What works for one person may not work for another, and that’s okay! The key is to find a way of eating that makes you feel your best and supports your individual health needs and goals.
The Bottom Line
Wow, we covered a lot of ground today! But I hope this gives you a better understanding of how nutrition can play a powerful role in managing chronic diseases and supporting overall health and wellbeing.
Remember, chronic diseases are not just something that old people have to worry about. By making healthy lifestyle choices, including good nutrition, we can all reduce our risk of developing chronic diseases and support our bodies’ natural healing processes.
If you or someone you know is living with a chronic disease, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider or registered dietitian for personalized nutrition advice and support. And most importantly, focus on nourishing your body with whole, minimally processed foods, staying active, and enjoying the journey!
Thanks for joining me on this nutrition and chronic disease adventure, my young and amazing friends. Until next time, keep exploring, keep learning, and keep fueling your body and mind with the good stuff. And if you ever have any questions, you know where to find me – I’m always here to help!












Leave a Reply